Overview
First, let's see the application demo https://www.snowpeak.org/math_question/ggb.htm
A snapshot of the application: 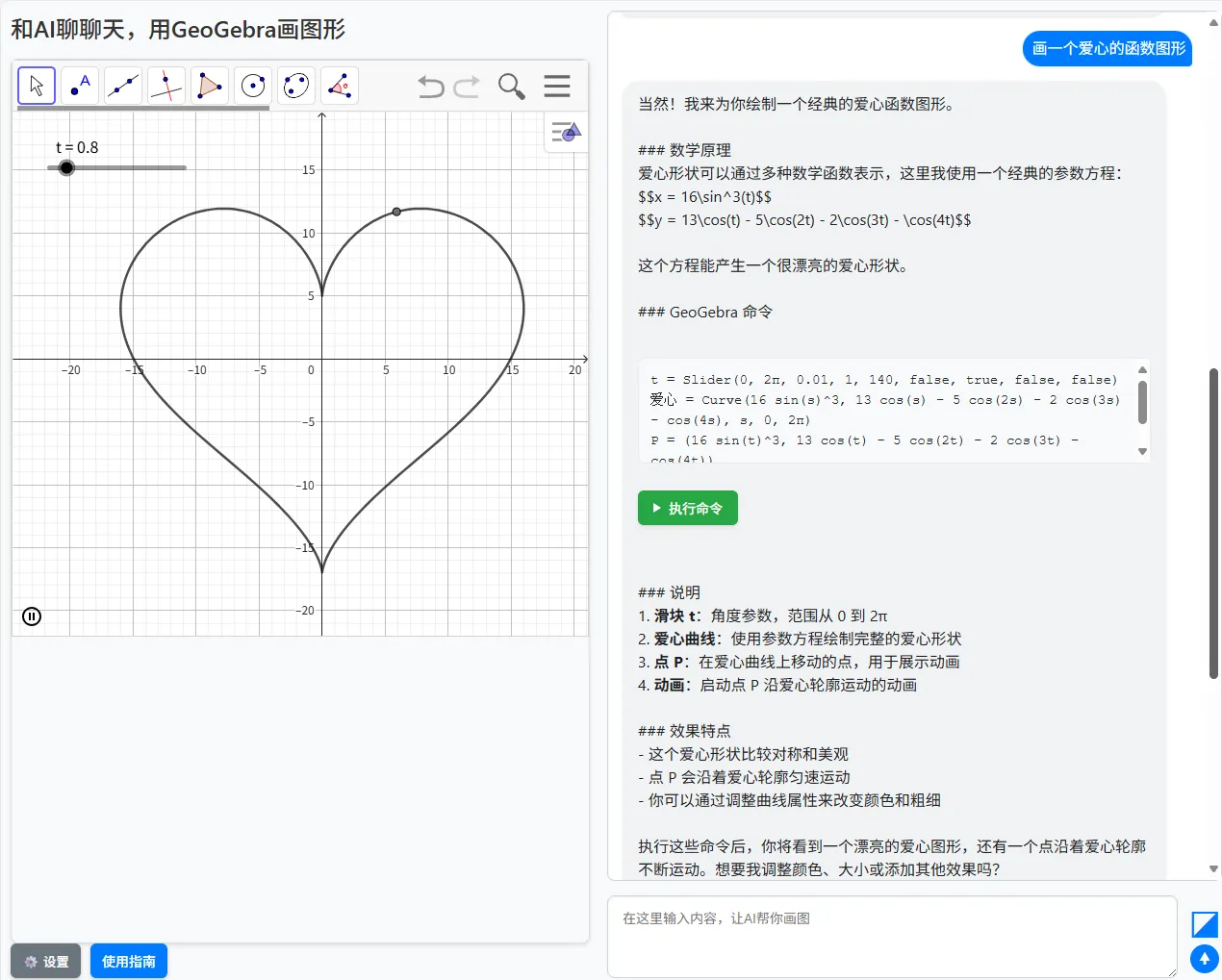
Project source code is open-sourced https://github.com/xfsnow/xfsnow.github.io/blob/master/math_question/ggb.htm
Who Should Read This Document?
This article provides an in-depth explanation of an intelligent tool - ChatGGB - that combines GeoGebra math software with AI chat functionality, covering its development process and implementation principles. It is suitable for friends interested in frontend development, AI integration, and mathematical visualization who understand basic JavaScript, HTML/CSS syntax and have some frontend development experience.
What Is This Document Useful For?
The content introduced in this document is suitable for large-scale frontend development projects, especially those involving AI integration, mathematical visualization, and user interaction design. By detailing the architecture and implementation of the ChatGGB project, it helps developers understand how to combine AI technology with mathematical software to create practical educational tools.
Significance
In the field of education and mathematical research, visualization is a very important tool. Traditional mathematical software requires users to master specific command syntax, while combining AI with GeoGebra can greatly lower the barrier to use, allowing users to interact with the system through natural language and automatically generate and execute mathematical commands. This not only improves user experience but also expands the application scenarios of mathematical software.
The significance of the ChatGGB project lies in: 1. Providing a new way of mathematical learning and research 2. Demonstrating how to integrate multiple AI models into a unified interface 3. Achieving seamless connection between AI and mathematical software 4. Providing new ideas for the development of educational technology
Project Background and Requirements Scenarios
Project Background
GeoGebra is an excellent mathematical software widely used in the field of education. However, using GeoGebra requires mastering its specific command syntax, which is a barrier for beginners. Meanwhile, with the development of AI technology, especially the continuous improvement of large language models in understanding and generating natural language, combining AI with mathematical software has become possible.
The ChatGGB project emerged to lower the barrier to using GeoGebra through natural language interaction, allowing users to generate and execute mathematical commands through simple language descriptions.
Requirements Scenarios Addressed
- Lower Learning Barrier: Users don't need to master complex GeoGebra command syntax, just describe requirements in natural language
- Improve Efficiency: Quickly generate and execute mathematical commands, saving manual input time
- Multi-Model Support: Integrate multiple AI models to meet different user needs
- Image Understanding: Support uploading images and analyzing and drawing based on image content
- Educational Applications: Provide intuitive visualization tools for mathematics teaching and learning
Code Architecture Design
Overall Architecture
The ChatGGB project adopts a pure frontend architecture, mainly consisting of the following parts:
- User Interface Layer: User interface implemented with HTML/CSS
- Control Logic Layer: Business logic implemented with JavaScript
- AI Interface Layer: Implementation of interfaces with different AI models
- GeoGebra Integration Layer: Implementation of interaction with GeoGebra
Core Class Design
The project adopts an object-oriented design approach, mainly including the following core classes:
AiBase Base Class
AiBase is the base class for all AI model classes, encapsulating common logic, including: - Message history management - System prompt processing - Image file to Base64 encoding - AI response formatting - GeoGebra command extraction
Specific AI Model Classes
The project supports three main AI models, each with a corresponding implementation class that inherits from the AiBase base class:
- AiDeepSeek - DeepSeek AI Class
- AiQwen - Qwen AI Class
- AiAzureOpenAI - Azure OpenAI AI Class
Each subclass implements specific calling logic according to the API specifications of their respective models.
GGBManager Class
This is the core management class of the project, responsible for coordinating various components, with main functions including: - Initializing GeoGebra application - Binding interface elements and events - Handling user input and AI responses - Executing GeoGebra commands - Managing settings and configurations
System Prompt Design
System prompts are a key part of guiding AI behavior and have special importance in the ChatGGB project. They not only need to guide AI on how to answer math-related questions but also need to specify how to generate GeoGebra commands.
Core Content of System Prompts
System prompts mainly include the following aspects:
- Role Definition: Clearly define AI's identity as a geometry assistant
- Behavioral Guidelines: Require AI to provide friendly explanations and clear GeoGebra commands when answering
- Command Format: Specify that GeoGebra commands must be placed in specific code blocks (
geogebra) - Mathematical Formula Format: Require mathematical formulas to be wrapped with $$
- Command Specifications: One command per line, no comments, arranged in logical order
System Prompt Sharing Mechanism
In ChatGGB, system prompts serve as global configurations that are effective for all AI models. Users only need to set them once to apply to all models, greatly simplifying the configuration process.
Dialog Interaction Methods
ChatGGB supports multiple dialog interaction methods to meet the needs of different scenarios:
Text-Only Dialog
Users can directly input text questions, such as "Draw a circle with radius 3", and AI will parse the question and generate corresponding GeoGebra commands.
Text and Image Dialog
For more complex scenarios, users can upload images and ask questions with text descriptions. This is particularly suitable for the following scenarios: - Uploading geometry problem images, asking for solution methods and drawing graphics - Uploading function graphs, requesting analysis of function properties and drawing similar graphs - Uploading real-world scene photos, requesting abstraction into mathematical models and drawing
This feature is mainly implemented by vision-understanding models such as Azure OpenAI's gpt-4o and Qwen's qwen3-vl-plus.
Image Processing and API Calls
Local Image Processing Flow
When users choose to upload images, the system performs the following steps:
- File Selection: Users select local images through the file picker
- Format Validation: Check file type (JPG/PNG/GIF/WEBP) and size (not exceeding 10MB)
- Encoding Conversion: Use FileReader to convert image files to Base64 encoding
- Preview Display: Display image preview in the interface
- Data Storage: Store Base64 encoding in shared state
Image Parameter Organization
When calling AI models that support vision understanding, images and text need to be organized into specific parameter formats:
// Construct user message containing image and text
const userContent = [
{ type: "text", text: "Please analyze the geometric shapes in this image and draw them" },
{
type: "image_url",
image_url: {
url: "data:image/jpeg;base64,/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQ..."
}
}
];
This structured approach allows AI to process both text and image information simultaneously, providing a richer interactive experience.
Main Principles of Calling Large Models
Unified Interface Design
The project implements a unified interface for different AI models by inheriting from the AiBase base class. The benefits of this approach are: 1. Clear code structure, easy to maintain and extend 2. Adding new AI models only requires inheriting the base class and implementing specific methods 3. Upper-level calling logic doesn't need to concern itself with the implementation details of specific models
Streaming Transmission Processing
To provide a better user experience, the project adopts streaming transmission technology to display AI's thinking process in real-time. This approach allows users to see AI's gradually generated responses rather than waiting for the complete response before displaying.
Multi-Model Support Mechanism
The project supports multiple AI models through a model selection mechanism, allowing users to choose appropriate models based on their needs. Each model has independent configuration items but shares global settings like system prompts.
Project Features and Advantages
Multi-Model Support
ChatGGB supports multiple mainstream AI models:
- DeepSeek: Open-source large model suitable for Chinese scenarios
- Qwen: Alibaba's Qwen series models, supporting image understanding
- Azure OpenAI: Microsoft Azure platform's OpenAI service
Image Understanding Capability
The project supports uploading images and analyzing them with AI, implemented through Azure OpenAI's gpt-4o model and Qwen's qwen3-vl-plus model. These models have powerful vision understanding capabilities, able to analyze mathematical content in images and generate corresponding GeoGebra commands.
Local Storage Configuration
User configuration information is persistently stored through localStorage, including API keys for each model and system prompts. This way, users don't need to reconfigure when visiting next time.
Summary
The ChatGGB project combines AI technology with GeoGebra mathematical software, providing users with a new way of mathematical learning and research. The project adopts a modular design with good scalability and maintainability, supporting multiple AI models and image understanding functions.
Through this project, we can see:
- The great potential of AI technology in the field of education
- The powerful capabilities of frontend technology in implementing complex interactions
- The important role of open-source technology in promoting educational innovation
In the future, this project can be further expanded, for example:
- Adding support for more AI models
- Providing richer visualization effects
- Enhancing interactivity and user experience
- Integrating with mathematical problem banks to achieve photo-based problem solving and accurate mathematical graphics drawing